Scheduling
Even when simply saying "scheduling," the rules required for the scheduler vary by industry, factory, and process.
- Prioritize processing urgent orders and execute other operations in the available time slots.
- Schedule with constraints on the timing of material arrivals and the skills and attendance schedules of each worker.
- In bottleneck processes, perform operations in an order that minimizes changeover setup time within the range where no overdue occurs, improving the overall throughput of the factory and making the preceding and succeeding processes just-in-time.
- In heat treatment processes, simultaneously process multiple lots with matching temperature conditions.
- Dispatch with different conditions for each process.
- Although product orders are for a wide variety of small quantities, produce common parts in large lots and peg them to each order.
- In the evening, fully load materials and tools onto the pallet changer and operate unmanned at night.
- Do not start new operations just before the end of the day's operations, and postpone them to the next day.
- Send items that have passed through the heating process to the next process before they cool down.
- In a certain process, process from light to dark colors, or from wide to narrow widths, in order.
- Plan with different rules for the next few days and thereafter.
To broadly respond to such diverse demands, FLEXSCHE GP allows you to freely define scheduling rules.
FLEXSCHE's scheduling rules are defined by combining "scheduling methods," which are the processing units of scheduling. Scheduling methods are, so to speak, "subroutines for production scheduling." Various settings can be made individually, and the behavior changes depending on the settings.

By effectively utilizing these mechanisms, you can perform scheduling like the following examples.
- First, assign each order backward to calculate the start date, then schedule forward.
- For finished products, produce to order, and for parts, produce in lots according to inventory status.
- If overdue occurs, manufacture through outsourcing.
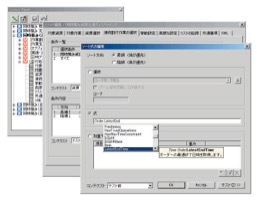
Scheduling rules are set from a dialog. If advanced condition definitions are required, they can also be expressed with formulas. Even in such cases, the input guide function allows for smooth setting. By using the scheduling panel, you can quickly access the desired setting items.
Operation-driven Dispatching Method
Select one from the operations to be assigned, then select one from the candidate resources and assign it. Repeat this chaining along the process sequence.
This is the most common and fastest method.
Resource-driven Dispatching Method

First, select the resource to be processed, then select from the list of operations assigned to it and assign. You can finely specify filtering conditions and priority criteria for target resources and target operations. You can control the order of operations, achieving productivity improvement in bottleneck processes by reducing setup time and consolidating specifications.
Elevating Control Resource-driven Dispatching Method

This is a resource-driven dispatching method made easier to use by limiting it specifically to elevating control order. It is used in cases where operations are performed while gradually adjusting temperature, size, shade, etc.
Simul-loading Resource-driven Dispatching Method

This is a resource-driven dispatching method that processes multiple lots with matching processing conditions such as temperature and variety simultaneously on one resource. It is used for batch consolidation in heat treatment furnaces.
Other scheduling methods include the following.
- Operation Generation Method
- Delete Objects Method
- Unassign Operations Method
- Assign result/frozen operations method
- Assign time anchored operations method
- Mark operations method
- Merge Operations Method
- Reassign forward method
- Reassign backward method
- Replenishment Order Generation Method
- Automatic Order Pegging
- Automatic Order Pegging Confirmation Method
- Automatic Order Pegging Cancellation Method
- Structurally control method
- Call external-method method
- Execute rule method
- Propagate result quantity method
- Split orders method
- Update initial inventory method
- Validate Data Method
- Modify Properties Method
- Execute commands method
and more
The mechanism for describing scheduling rules is highly flexible, and in many cases, problems can be solved by combining existing scheduling methods. Even when special processing is required, you can define rules by programming your own scheduling methods, allowing you to mix standard functions with custom processing. Scheduling processes that could not be realized with conventional package software can be achieved by simply developing the differences.
