FLEXSCHE version 18
FLEXSCHE version 18.0 was released on October 15, 2018. It includes approximately 221 feature enhancements. Here are some of the main ones. (Differences between version 17.0 and version 18.0)
User Interface Data & Modeling the Workshop Planning Option FLEXSCHE Communicator FLEXSCHE EDIF Expression Programming Related (For Developers) Other
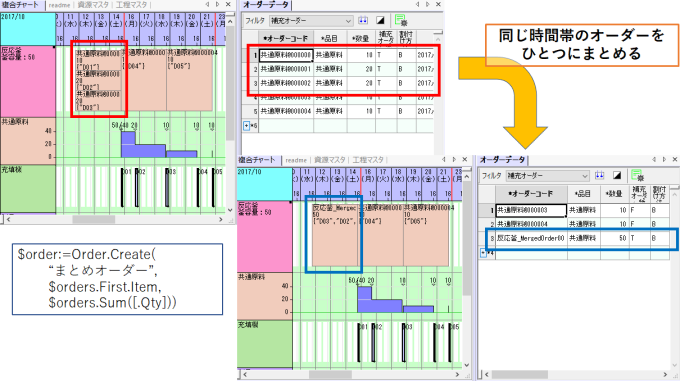
Batch Search Function
It is now possible to perform a batch search across the entire FLEXSCHE using various conditions.
Various Search Conditions

Search Destination List
Using the batch search dialog, you can search the entire FLEXSCHE with conditions such as the following.
- Partial String Match
- Regular Expressions
- Conditional Expressions for Objects
- Enumerated Objects
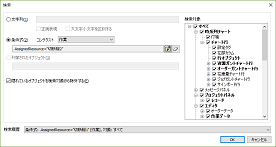
Search Dialog
The search results are displayed in a list on the search panel.
You can also select and limit the search range within the batch search dialog. Alternatively, the search range can be implicitly limited by the location where the batch search dialog is launched (such as the project panel or timeline chart menu). Conversely, by launching from a specific object (such as an object in the project panel), you can quickly find where it is displayed.
Since the search history is retained, you can quickly re-execute searches with the same conditions.
Jump from Search Results
By double-clicking an item in the search panel, the position on the window of each search destination is highlighted, making it easy to find the target.
Available from Add-ins
The batch search framework can also be used from third-party add-ins. You can add the display content of your own add-ins, views, and panels to the search target and implement actions when the relevant item is double-clicked in the search panel.
Alternative Job Function
Hierarchical process definitions have enabled more flexible master data operations and adaptation to variations in process flows.
* The advanced option "Alternative Job" (2 units) is required.
It is now possible to use the "Alternative Job" function, which deploys and assigns a series of operations instead of a single operation. This makes it easier to operate by dividing process definitions by hierarchy. Additionally, it is possible to automatically select one from multiple alternative production methods with different numbers of processes.
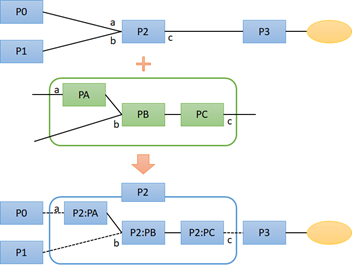
In the diagram on the right, a process graph (PA→PB→PC) is specified for deploying alternative jobs in process P2. Through automatic scheduling, a series of operations (P2:PA→P2:PB→P2:PC) is deployed as an "Alternative Job" under operation P2 and assigned in place of P2.
For example, when the granularity of processes managed by the core system and scheduling differs, detailed process definitions can be added only on the FLEXSCHE side without changing the process definitions on the core system side. Even if there are changes in the process definitions on the core system side, you only need to add detailed process definitions to those parts on the FLEXSCHE side, requiring minimal modifications.
Also, in cases where manufacturing must begin before detailed processes are finalized in make-to-order production, using alternative jobs allows you to separate basic and detailed process definitions and smoothly replace them in order as detailed processes are finalized.
Multi-stage Deployment
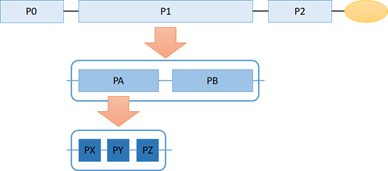
If a process graph for deploying alternative jobs contains processes with further alternative job deployment specifications, the alternative jobs are deployed in multiple layers.
For example, when processes are hierarchically managed as in large schedule → medium schedule → small schedule, it is possible to smoothly perform multi-stage operations that inherit process definitions and planning content from the upper hierarchy while independently detailing them in the lower hierarchy.
Additionally, it is highly compatible with WBS (Work Breakdown Structure) in project management.
Automatic Selection from Multiple Production Methods
When multiple process graph candidates for alternative jobs are specified, they become exclusive options. In this case, automatic scheduling automatically selects and assigns one of these candidates. The selection criteria can be finely specified using expressions.
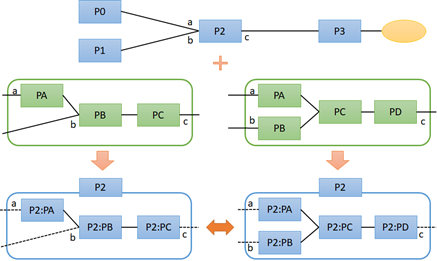
In the diagram on the right, there are options consisting of three processes (PA→PB→PC) and four processes (PA・PB→PC→PD) for process P2. The most desirable option among these is automatically adopted through automatic scheduling.
This allows for planning that automatically adopts the more desirable option, even when there are multiple production means with different numbers of processes, such as in-house production and outsourcing.
User Interface
[Each Chart Row] Directly Open the Chart Format String Editing Screen
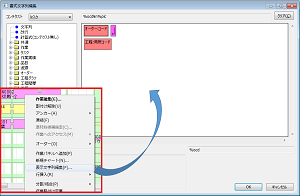
It is now possible to directly call up the format editing screen from the popup menu of the location where you want to edit the string, such as the left section of the resource Gantt or tasks on the Gantt chart.
This is particularly effective when it is cumbersome to reach the desired display string editing dialog due to overwrite display settings, branching, or using multiple columns.
[Entire Chart] Display Settings for Multiple Column Labels by Double-clicking
By double-clicking the column name part of multiple columns, you can now open the column settings screen for the entire chart.
[Entire Chart] Specify Setting Tags for Row Configuration Rules with Expressions
It is now possible to express the specification of setting tags embedded in each row with expressions. This allows for flexible chart expressions when combined with costumes, etc.
[Entire Chart] Refer to Stored Variables of Chart Rows from Expressions
With the TimeChartRow.VariableValue function, you can now refer to stored variables. This allows for usage methods such as keeping values aggregated in upper rows and referring to them in lower rows. This improves processing cost performance compared to aggregating each time in lower rows.
[Resource Gantt Chart] Background Color of Separated Task Strings
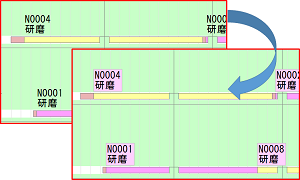
When task strings are separated from the bar, it is now possible to set their background color.
[Resource Gantt Chart] Select Tasks with Separated Task Strings
Even when clicking the string part, it now selects the task in the same way as clicking the task.
[Resource Gantt Chart] Display of Date and Time Comments

When task strings are separated from the bar, it is now possible to display arbitrary comments keyed by date and time.
[Inventory Level Chart] Specify the Range of the Inventory Level Chart with Num-Spec
It is now possible to specify the range (value range of the vertical axis) with item num-spec.
[Signboard] Enhanced Display Functionality of Data Cube

When displaying the contents of a data cube, it is now possible to specify the text color according to conditions. In addition to outputting the value of the data cube as is, it is now possible to convert it arbitrarily via expressions. Also, in display by expressions, it is now possible to specify the text color.
[Operation Sequence Chart] Enhanced Display of Row Headers
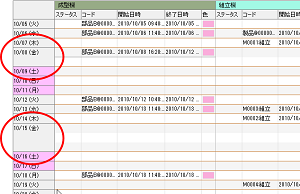
When displaying with day breaks, row headers for the same day are merged. Also, the day of the week is now displayed.
[Expression] Copy & Paste Support for Conditional Content Parts
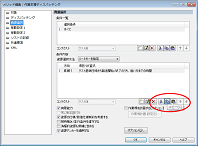
Copy & paste support has been added for conditional content parts such as resource selection in operation-driven dispatching.
[Expression] Multi-line Calculation Formula Input Field
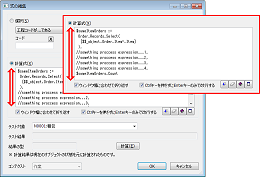
Previously, to input a multi-line calculation formula, a separate dialog had to be opened for that purpose, but now it is possible to directly input multiple lines in the calculation formula input field. Also,Variable Sizehas been implemented, allowing for even larger use of the calculation formula field.
[Expression] Support for Tab Insertion
Indent operations for readability are now possible. You can insert Tab or Space indents collectively by selecting multiple lines, or reduce indents with Shift+Tab.
[Skill Editor] Continuous Input of Skill Names
When entering a skill name in the Skill Editor, you can now quickly and continuously move between columns using the Tab key and input the skill name from the keyboard.
[Data Window] Paste Values
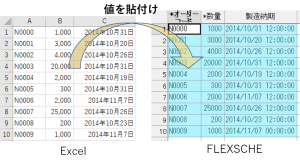
It is now possible to paste data from Excel while considering the data type. Even if the format, such as date and time, differs due to formatting settings, it will automatically paste while considering the type.
[Operation Data Window] Change Selection State from Master Edit Screen
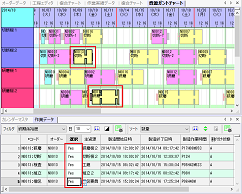
You can now change the selection state of operations on the chart from the operation data edit screen. By utilizing the filter and sort functions of the master screen, you can change the selection state of extracted operations and manipulate them on the chart.
[Others] Full Screen Display
A full-screen mode has been added, allowing you to display only the view to fill the entire screen.
[Others] Resizable Property Page
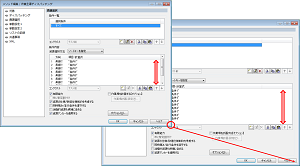
Some dialogs that were previously fixed in size have become resizable. The size of lists and edit boxes will now adjust with the screen size, allowing more information to be displayed when enlarged.
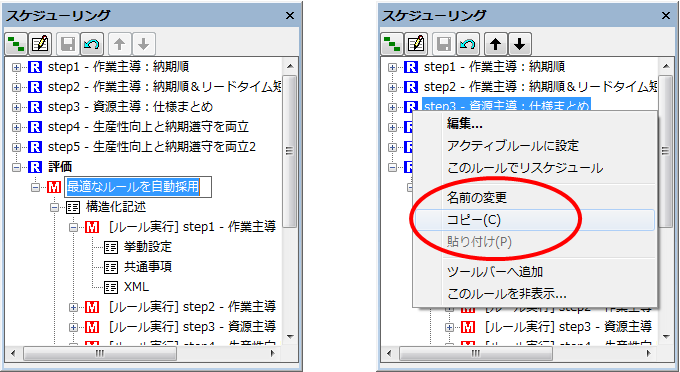
[Others] Scheduling Panel Expansion
You can now edit rule names/method descriptions and copy & paste rules/methods directly from the scheduling panel. Additionally, methods within structured descriptions are displayed, allowing you to open the method edit dialog directly without intermediate dialogs.
Data & Modeling
Added Special Skill Key
Even if the skill you want to apply is complex, it can now be easily specified.
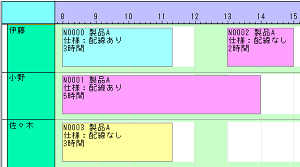
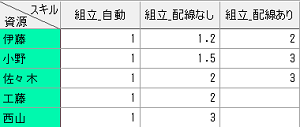
In FLEXSCHE, you can specify "skills" for each worker to realize a model where abilities differ by worker, and even when manufacturing the same item, the time may vary, or some people may not be able to perform the work at all. Previously, when the skill you wanted to apply changed depending on the situation, such as when the specification changed for the same item, it was necessary to describe complex formulas. However, in the new version, it has become possible to express such a model easily without formulas.
Indirect Specification of Spec Key within Combo Key
It has become possible to more flexibly limit the combination of machines, tools, and people for performing work.
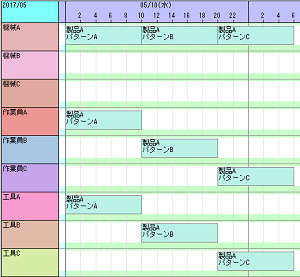
For example, there are cases where a certain operation can be performed with either machine A or machine B, but if using machine A, tool A must be used simultaneously, and if using machine B, tool B must be used simultaneously. Such combinations can be easily specified using a "combo key," but previously, only fixed combinations could be given for each item. In the new version, it has become possible to specify different combinations for the same item depending on the situation more flexibly.
Proper Time Constraint Coefficient Key
It has become easy to change the buffer time between processes according to the situation.
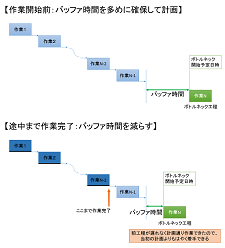
To accommodate fluctuations during execution,Buffer Timecan be planned in advance between processes, and it has become possible to parameterize that buffer without formulas. This allows for easily reducing buffer time when it is judged that fluctuations have decreased according to the progress of the work, even if a larger buffer time was initially taken before starting the work.
Yield Coefficient Key
It has become possible to specify yield more flexibly.
Previously, only fixed values could be specified for yield for each item and process, but it has become possible to set it dynamically. This makes it easier to express a model where yield varies depending on the resources used, even for the same item.
AND Specification for Multiple Selectors on the Selected Side
Expressing process variations has become easier.
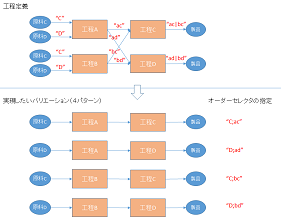
[Example 1] Conventional Specification Method
Regarding selectors,as explained in detail in previous new feature introductions,it has been further improved to allow multiple selectors to be specified with AND on the selected side. This can simplify the specification of selectors in some cases.
In [Example 1], there are four patterns where the preceding process can be either process A or B, and the subsequent process can be either process C or D. Furthermore, the raw materials to be input in the preceding process change depending on whether process C or D is used in the subsequent process.
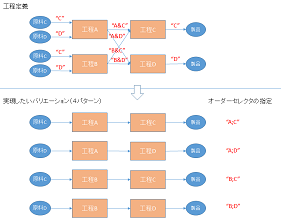
[Example 2] Specification Method Using AND
Previously, it was necessary to prepare four selectors (ac, ad, bc, bd) for process selection and two selectors (C, D) for raw material selection and specify them appropriately from the order.
With the ability to specify multiple selectors with AND on the selected side as in [Example 2], it becomes possible to choose and specify which process to go through from four selectors (A, B, C, D).
Generate Operations from Results
It has become possible to generate new operations from operation results and assign them on the chart.
Usually, to generate operations and plan, a master of processes, resources, and capabilities is necessary, but even without these masters, it has become possible to generate operations and assign them on the chart by providing actual information on when (from what time to what time) and where (with which machine/person) the work was done.
For example, it becomes possible to consider loads and plan even for unplanned operations that are not managed as masters.
Subdivide Item Groups
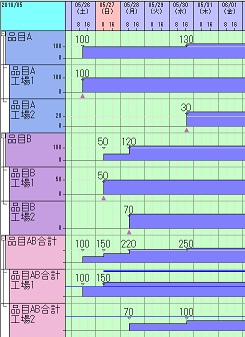
It has become possible to subdivide item groups.
This allows for aggregating the inventory level of each item belonging to an item group by location. For example, you can check in the inventory level chart whether the total inventory level of multiple items exceeds the maximum allowable amount for each factory and plan to ensure it does not exceed.
Default Values for Custom Fields
It has become possible to set default values for custom fields (user-defined fields). When adding records from EDIF or add-ins, you can omit the setting if you adopt the default value.
the Workshop Planning Option
The "Workshop Planning Option," which allows for automatic scheduling and manual adjustment while considering the constraints of item placement, has been significantly expanded in functionality.
Speedup through Parallel Processing
The workshop planning function can now be parallel processed. Scheduling time can be reduced in a multi-core CPU environment.
Specification of Evaluation Criteria for Placement
Previously, the placement of the workshop was automatically determined, but it has become possible to specify a formula for evaluating each placement candidate. For example, you can reflect detailed intentions in the plan, such as "preferentially place as close to the aisle as possible."
If the placement is not desirable, move to the next time slot or another workshop.
In the resource selection and re-search start point of the Operation-driven Dispatching Method, it has become possible to refer to the planned placement in the workshop. This allows you to move to the next time slot or prioritize other workshop resources if the planned placement is not desirable.
Release Rectangular Restrictions on Placement Area
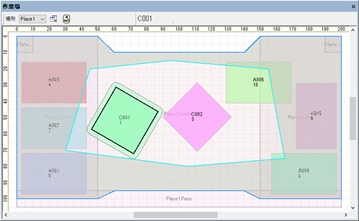
Previously, even if a polygon was specified for the shape of the limited area of the workshop or area constraints, they were considered rectangles during placement planning, but now they are placed within the polygon.
Mesh Size Specification
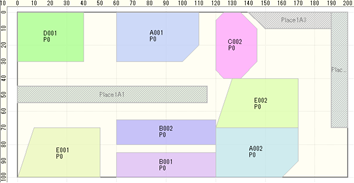
It has become possible to specify the mesh size of the placement position. For example, it can be placed according to the section if the placement location is divided into equally spaced sections.
Overlay Images on Workpiece
It is now possible to overlay individual images on each workpiece placed in the workshop panel. Not only the contours of the workpiece but also the internal conditions can be displayed realistically.
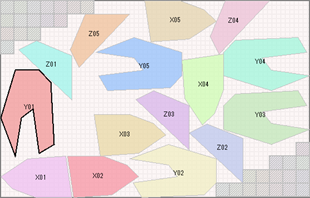
Normal
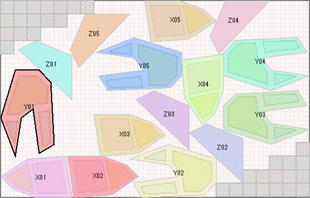
Overlay Images on Workpiece
Display coordinates within the workshop
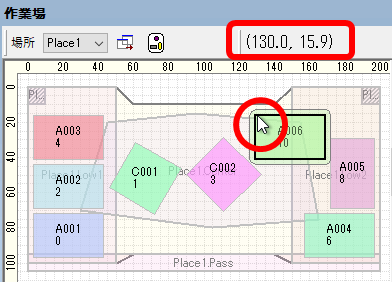
The coordinates of the workshop at the mouse cursor position can now be displayed in the status bar of the workshop panel. This is convenient for checking the coordinates in various locations within the workshop.
Display string and color of sub-areas
It is now possible to set display strings and colors for sub-areas included in the workshop on the workshop panel.
Export background as well
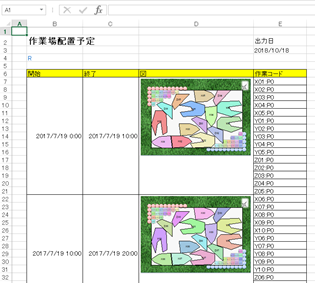
When exporting a workshop to an EMF file (Enhanced Metafile) or SVG file (Scalable Vector Graphics) using EDIF, the background is also output. By setting an appropriate background, visibility in work instructions, etc., can be improved.
Dropdown to the workshop panel
It is now possible to drag and drop operations from the operation panel or project to the workshop panel to change placements. This allows for smooth operations such as moving operations placed in another workshop and specifying further placements.
Skip non-operating hours in the workshop panel
When switching the display time range back and forth in the workshop panel, it is now possible to skip non-operating hours such as holidays.
FLEXSCHE Communicator
Advanced option settings for each project service
It is now possible to set different advanced options for each project service registered in Communicator. As long as it is within the range of the number of advanced options held, multiple projects with different requirements can be used with the same license.
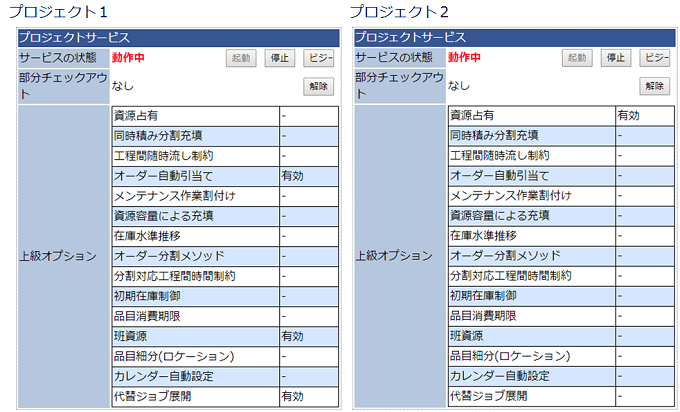
Speedup through Parallel Processing
By enabling parallel processing in scheduling on the server, it is now possible to speed up the process.
Use external methods/functions in scripts
It is now possible to execute script add-ins on Communicator. Various functions can be easily implemented without preparing a full-fledged development environment and creating DLLs.
FLEXSCHE EDIF
Support for SAP HANA
NewlySAP HANAintegration has become possible. HANA is a new RDBMS that has begun to be adopted in ERP and MRP, among others. With FLEXSCHE now supporting HANA, direct integration with core systems that have adopted HANA has become possible.
Support for JSON format
Support for file I/O in JSON format has been newly added. JSON files are convenient for access from scripts, etc., and are useful when processing data obtained by EDIF with an intermediate step.
Reference the previous record in EDIF import
It is now possible to reference the record imported one entry before. For example, it will be easier to control behavior when reading aligned data sequentially and detecting changes in the values of specific columns.
More detailed rollback specification during EDIF import
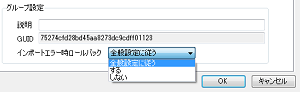
Previously, there was only a common setting for the entire process to specify "rollback/do not rollback" in case of an error, but now it can be specified for each import group.
Expression
Extension of random number functions
The Math.Random function has been extended to allow specifying the method of generating random numbers. You can choose according to the desired speed and quality. Additionally, functions for generating random numbers with normal distribution and Poisson distribution have been added.
It is considered for use in applications such as simulations.
Calculation formula objects
It is now possible to assign function-type values to variables like lambda expressions. Common routines can be defined within the calculation formula without using the calculation formula library as before, improving readability and maintainability.
Example) Compare the earliest start time of split sibling operations
$earliestStart := Operation()[
.SplitBase.SplitOperations
.Select([.IsAssigned])
.Min([.ManufactureStartTime]) ],
.PrecedingOperation.$earliestStart() < .$earliestStart()
Recursive functions and mutually referencing functions can also be described without using the calculation formula library.
Example) Fibonacci numbers
$fib := (Long n)[$n <= 1 ? $n : $fib($n - 2) + $fib($n - 1)]->Long, $fib(10)
Record generation functions
Functions for generating records have been added. It is possible to generate arbitrary operations, orders, free calendars, operation results, and operation connection records. For example, you can generate orders to consume according to inventory or generate one order and consolidate multiple orders. These functions can only be used within the property generation method.
Dynamically fetch variable values
A Variable function has been added to fetch variable values in a calculation formula instead of literals. It can be used when you want to change the variable name to be fetched according to the situation or dynamically reference EDIF parameters from reports.
Various functions added
The number of functions that can be used in calculation formulas has further increased, expanding the possibilities even more.
Programming Related (For Developers)
FLEXSCHE is not only equipped with comprehensive functions as a packaged software but also has the significant feature of easily adding functions through programming.
Extension of button control behavior in FLEXSCHE Scripting forms (FSF)
FLEXSCHE Scripting forms is a framework for easily creating modal and modeless forms (views/panels) using only scripting languages (JavaScript/VBScript). In version 18.0, the following feature extensions have been implemented.
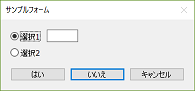
Set the default button to "No"
It is now possible to specify the button (default button) that is considered pressed when the Enter key is pressed in a modal form (Yes/No or Yes/No/Cancel).
Display Implementation Example
Sub SampleForm_Initialize( form ) ... form.Property( "form", "default_button")="no" ... End Sub
It is now possible to disable the Enter key and Escape key in modal forms.
Display Implementation Example
Sub SampleForm_Initialize( form ) ... form.Property( "form", "accept_enter")=false form.Property( "form", "accept_escape")=false ... End Sub
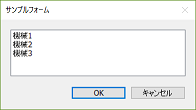
Double-clicking a list item
is equivalent to pressing "OK"
In a modal form, it is now possible to close the form by considering a specific button (OK/Cancel/Yes/No) as pressed within any event processing.
Display Implementation Example
Function SampleForm_Event( form, ctrl, evnt, param )
...
if ctrl = "list1" then
if evnt = "double_clicked" then
form.Done "ok"
end if
end if
...
End Function
Other
Reading simplified date notation
Previously, only dates with a four-digit year like "2018/11/23" could be interpreted, but now two-digit years like "18/11/23" are also accepted.
